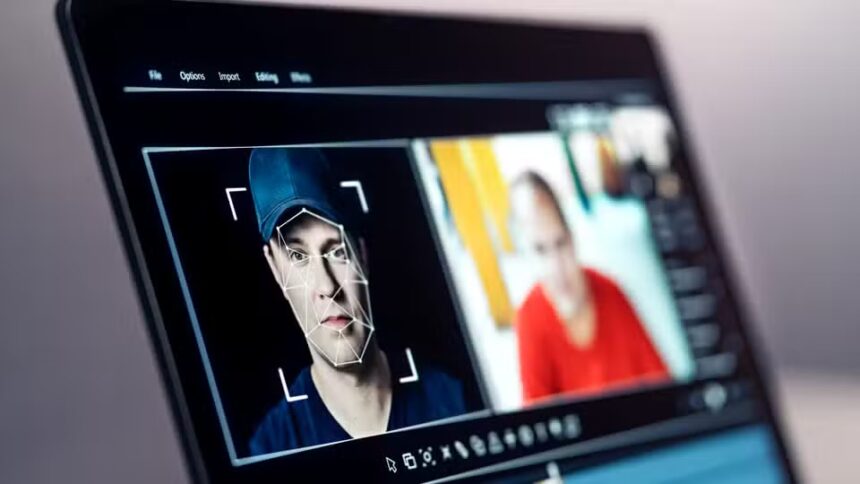
From deepfakes to misleading edits, it’s becoming increasingly difficult to tell what’s real and what’s fake. That’s why verifying images and videos online with AI has become an essential skill for journalists, researchers, content creators, and everyday internet users.
Artificial intelligence tools can help you detect inconsistencies, trace original sources, and confirm authenticity within seconds; saving you from misinformation traps.
Below is a detailed, step-by-step guide that explains how to effectively verify visual content online using AI-powered tools, best practices, and expert tips.
Step 1: Understand Why Verification Matters
Before you start, it’s important to understand why verification is critical. Fake visuals can distort public opinion, damage reputations, and spread harmful propaganda.
AI-driven verification doesn’t just help debunk false content, it strengthens online credibility. Whether you’re fact-checking viral clips or validating images for a publication, accuracy ensures your audience receives trustworthy information.
Step 2: Choose the Right AI Verification Tool
There are numerous platforms that assist in verifying images and videos online with AI. Some of the most reliable include:
- Google Lens and TinEye for reverse image searches
- InVID for video verification and frame analysis
- Deepware Scanner for detecting deepfakes
- Microsoft Video Authenticator for identifying AI-generated media
- Reality Defender or Sensity AI for comprehensive authenticity scoring
Each tool serves a different purpose, so use a combination for more accurate results.
Step 3: Start with a Reverse Image or Frame Search
Upload the image or a video frame into a reverse search engine like Google Lens or TinEye. This will show you where else the image has appeared online, when it was first indexed, and whether it has been used in misleading contexts. If you’re verifying a video, extract keyframes using a tool like InVID and check each one separately.
Step 4: Examine Metadata and Context
Most images and videos contain embedded metadata, information about when, where, and how the media was created.
Tools like ExifTool and FotoForensics can help you uncover EXIF data, including timestamps, device details, and geolocation. Inconsistent or missing metadata can be a red flag, especially if a photo claims to come from a recent event.
Step 5: Use AI Deepfake Detectors
If you suspect a video might be manipulated, AI-based deepfake detection tools can analyse subtle signs of tampering such as unnatural blinking, lighting mismatches, or face-swapping artefacts.
Upload the video to a trusted service like Deepware Scanner, Hive Moderation, or Sensity. These tools provide authenticity scores and highlight possible manipulated frames.
Step 6: Check the Source and Social Context
Always cross-check where the media originated. AI tools can help trace the first upload or identify manipulated reposts.
Combine this with social network verification, look for who shared the content first, whether the account is verified, and how other credible sources are responding.
Step 7: Evaluate Visual and Technical Clues
Even with AI assistance, human judgment is vital. Examine the visual content closely for inconsistencies in lighting, reflections, shadows, and proportions.
AI tools can enhance this by highlighting irregularities invisible to the naked eye, but you should confirm with manual inspection before drawing conclusions.
Step 8: Combine Multiple AI Results for Confirmation
No single AI tool is foolproof. Combine results from several verification services to get a clearer picture. If three or more tools return similar findings; for example, confirming that a video was first posted years earlier, you can confidently classify it as misattributed or manipulated.
Step 9: Document and Report Findings
When verifying for professional or research purposes, always document your steps and sources. Record screenshots, URLs, and timestamps for transparency. If you uncover disinformation, report it to relevant platforms or fact-checking organisations like AFP Fact Check or Reuters Fact Check.
Step 10: Stay Updated on New AI Tools
AI verification technology evolves rapidly. Stay informed about the latest detection methods and updates from research labs or platforms like MIT Media Lab and Deeptrace. Regularly testing new tools ensures you remain ahead of emerging synthetic media trends.
FAQs on Verifying Images and Videos Online with AI
What does verifying images and videos online with AI mean?
It means using artificial intelligence tools and algorithms to analyse digital media for signs of manipulation or misrepresentation. These AI systems can detect inconsistencies in lighting, metadata, pixels, or motion patterns that indicate whether an image or video has been altered, deepfaked, or taken out of context.
Can AI detect all types of fake or edited content?
No, AI isn’t perfect. While AI tools can detect many forms of tampering such as deepfakes or composited images, they might miss subtle manipulations. That’s why human verification, contextual analysis, and cross-checking results from multiple tools are still necessary for accurate conclusions.
What are the best free AI tools for verifying images and videos?
Some reliable free tools include Google Lens, TinEye, and InVID for image and video searches. For detecting deepfakes, Deepware Scanner and Sensity AI’s free analysis features are good starting points. Combining these tools gives you broader and more precise verification coverage.
How accurate are AI deepfake detectors?
Accuracy varies depending on the quality of the input and the complexity of the manipulation. Most reputable detectors, like Deepware Scanner or Microsoft Video Authenticator, have accuracy rates between 85% and 95% for standard deepfakes.
Is verifying media with AI safe and private?
Most trusted AI verification tools prioritise data privacy and don’t store your uploads permanently. However, always read the tool’s privacy policy before uploading sensitive media. When possible, use offline verification software or anonymised browsers to ensure your personal data isn’t collected or reused.